Friday, 28th May 2021
Right to be forgotten - Edukemy Current Affairs
In News
Delhi High Court recently upheld the Right to be Forgotten of American citizen and directed the search engine Google and website Indian Kanoon to block an acquittal judgment.

About the News
- Taking note of the irreparable prejudice that may be caused to the individual’s social life and his career prospects despite him having been ultimately acquitted, the Delhi High court upheld the right of an individual to be forgotten while granting interim relief to the American citizen of Indian origin who was acquitted of criminal charges.
- Google has been asked to remove the judgment from its search results and Indian Kanoon has been directed to block the judgment from being accessed by using search engines such as Google and Yahoo.
What is the Right to be Forgotten (RTBF)?
- The ‘right to be forgotten’ is the right to have publicly available personal information removed from the internet, search, databases, websites, or any other public platforms, once the personal information in question is no longer necessary, or relevant.
- The right to be forgotten has been recognised as a statutory right in the European Union under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and has been upheld by a number of courts in the United Kingdom, and in Europe.
- In India, there is no law that specifically provides for the right to be forgotten. However, the Personal Data Protection Bill 2019 recognised this right.
When can the right be exercised?
- In the right to privacy judgment, the Supreme Court had clarified that the recognition of this right “does not mean that all aspects of earlier existence are to be obliterated, as some may have a social ramification”.
- The SC explained: “If we were to recognise a similar right, it would only mean that an individual who is no longer desirous of his personal data to be processed or stored, should be able to remove it from the system where the personal data/information is no longer necessary, relevant, or is incorrect and serves no legitimate interest.”
- The apex court asserted that this right cannot be exercised where the information or data is necessary for: (1) exercising the right of freedom of expression and information; (2) compliance with legal obligations; (3) the performance of a task carried out in public interest, or public health; (4) archiving purposes in the public interest; (5) scientific or historical research purposes or statistical purposes; or (6) the establishment, exercise, or defence of legal claims.
Land Bank Company
In News
The Department of Investment and Public Asset Management (DIPAM) is working to seek approval from Cabinet to set up a land bank company.
Details of the news
- DIPAM has finalized the structure of the company that will be tasked with selling land parcels —including those stuck in litigation —owned by government departments and public sector companies.
- The proposed SPV by DIPAM will help to utilize better land parcels of PSUs and develop them into revenue generating projects by selling them to investors through attractive arrangements.
- The public sector has not been able to sell land assets due to litigation and lease terms. The proposed SPV will house experts to resolve these disputes and then monetize these lands.
- It will be based on the Canadian model (Canada Lands Company) which is a government entity that can dispose of and monetize the surplus land of government departments and at the same time specialize in real estate and managing assets such as tourist destinations.
- It is in pursuant to the Union Budget 2021-22 proposal to launch a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) for monetization of land belonging to the Government-owned companies and PSUs by way of direct sale, concessions, or other suitable means.
|
Land Bank and its benefits · A land bank includes large tracts of land kept under the control of governments or private organizations for future development. Land banks can be used for setting up industrial projects like a dam. · In 2018, NITI Aayog had advocated for the creation of land banks by states to ensure ease of business and encourage industry. · A 2020 Report by the Land Conflict Watch (LCW), a New Delhi-based research group highlighted that up to 2.68 million hectares of land has been set aside for land banks in eight states – Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, and Uttar Pradesh. Benefits · Complexity of land acquisition which involves huge conflicts in terms of compensation, displacement of locals and loss of agriculture lead to high-worth projects getting shelved. E.g., POSCO steel project in Odisha. · In such a scenario, land banks have emerged as an important tool to attract industry and investment because most land parcels (in the land banks) already have most of the required clearances. o This facilitates smooth set up of industrial projects without delay and bureaucratic procedures. Challenges with Land Bank · Land banks act as a bypass mechanism to deny the rights of tribal and other communities. · In many cases, common lands over which communities had traditional rights have been set aside as part of land banks. This hampers communities’ ability to claim rights over it under laws such as the Forest Rights Act (FRA). · Lack of digital land records and maps of land creates challenges of identification of right beneficiary to compensate for land acquisition. |
Satellite communication
In News
The government has removed the artificial caps on the data rates that the global satellite communication companies can offer, which were pegged at speeds of 2Mbps to 4Mbps.
About the News
- Amendments have been made to the Standards for Interface Requirements for Communications and Broadcast Networks issued by the Telecom Engineering Centre (TEC) under the Department of Telecommunications to do away with the legacy regulation of a low data speed limit. This is applicable to all satellite communication services companies in the country.
- The TEC’s amendment allows satellite communications services to use the high-capacity Ka band between 27 Ghz and 40 Ghz (currently, they are allowed to use only C and Ku bands) for both broadband and broadcasting services by direct-to-home (DTH) operations. This will allow companies to provide high-speed broadband and help DTH operators offer many more channels and very high-resolution display.
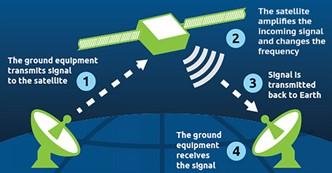
What is Satellite Communication?
- Satellite communication, in telecommunications, refers to the use of artificial satellites to provide communication links between various points on Earth. Satellite communications play a vital role in the global telecommunications system. Approximately 2,000 artificial satellites orbiting Earth relay analog and digital signals carrying voice, video, and data to and from one or many locations worldwide.
- Components: Satellite communication has two main components: the ground segment, which consists of fixed or mobile transmission, reception, and ancillary equipment, and the space segment, which primarily is the satellite itself.
- Mechanism: A typical satellite link involves the transmission or uplinking of a signal from an Earth station to a satellite. The satellite then receives and amplifies the signal and retransmits it back to Earth, where it is received and reamplified by Earth stations and terminals. Satellite receivers on the ground include direct-to-home (DTH) satellite equipment, mobile reception equipment in aircraft, satellite telephones, and handheld devices.
- India’s Satellite Communication system: The Indian National Satellite (INSAT) system is one of the largest domestic communication satellite systems in Asia-Pacific region with nine operational communication satellites placed in Geo-stationary orbit. Example: - INSAT-3A, 3C, 4A, 4B, 4CR and GSAT-6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17 and 18.
https://www.britannica.com/technology/satellite-communication
Solar geoengineering
In News
Bill Gates and Harvard University are planning to back solar geoengineering to fight global warming.
About the News
- Known as the Stratospheric Controlled Perturbation Experiment (SCoPEx), it is a scientific experiment to advance understanding of stratospheric aerosols that could be relevant to solar geoengineering.
- SCoPEx will address questions about how particles interact with one another, with the background stratospheric air, and with solar and infrared radiation.
- Improved understanding of these processes will help us understand the possibility of aerosols to reduce or eliminate ozone loss or stratospheric heating, without increasing other physical risks.

What is Solar geoengineering and why is it needed?
- Solar geoengineering is a specific form of albedo modification in which highly reflective particles are introduced into the atmosphere to increase Earth’s albedo. This would reduce incoming light (radiation) from the sun, and thereby decrease the amount of energy (heat) reaching Earth’s surface.
- Worsening state of Global Warming: Adverse effects of global warming threatens public health, food security, housing and water availability, and national security. So, the need for actions with quick effects like geoengineering becomes pertinent in the short term, along with long term plans of emissions reduction and forest conservation.
- The current climate change commitments are not enough: The ambitious goals under the Paris Agreement may fall short because they may not be enough to limit warming to the levels needed to avoid catastrophic consequences. Even if the temperature increase is limited to 1.5°C, the world would still face severe climate risks.
- Potential of Solar Geoengineering: The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has acknowledged that the aerosol injection in the stratosphere or SRM could reduce some of the global risks of climate change related to temperature rise, rate of sea level rise, sea-ice loss, and frequency of extreme storms. Such mitigation and adaptation can act as our first-line solutions.
- High Vulnerability of countries: Countries in the global south like India are likely to be the worst hit by climate change. Economies like India that are massively dependent on the monsoon are vulnerable to changes in weather, both by climate change as well as potential after-effects of technologies such as solar geoengineering.

Challenges in its implementation
- Unpredictability and moral hazard: Opponent of solar geoengineering claim that it can create unpredictable results and then could be difficult to safely shut it down. There are also concerns of moral hazard, as the technology may become an excuse to slow emissions reductions and stop moving toward a low-carbon economy.
- Addresses only the symptom, not the disease: Solar geoengineering does not address the underlying problem of climate change i.e., the build-up of greenhouse gases or some of the resulting impacts, such as ocean acidification.
- Lack of collaboration and support: The Stratospheric Controlled Perturbation Experiment (SCoPEx) had to cancel a balloon flight. Until now, public bodies have not prioritized reaching such a consensus on geoengineering.
- Introduces unknown climate risks: Very little is known about how it could impact regional weather patterns, global politics and efforts to curb global warming emissions. Also, it may have regional and global implications as outdoor experimentation is a difficult subject to address.
Conclusion:
Solar-geoengineering research brings risks, and there are other, more-promising ways to address global warming. But the world remains on a path to dangerous climate change, and future generations will bear an increasing burden. Governments need to step up climate efforts and evaluate all possible options for action. If solar geoengineering is harmful, leaders will need evidence so that they can rule out the technology.
Question: What is solar geoengineering? Discuss the advantages and disadvantages associated with this technology.
https://www.ucsusa.org/resources/what-solar-geoengineering
https://www.carbonbrief.org/explainer-six-ideas-to-limit-global-warming-with-solar-geoengineering
Secondary Sources: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-01243-0
https://geoengineering.environment.harvard.edu/geoengineering
This Day in History International Day of Action for Women’s Health
Since 1987, May 28th has been commemorated as the International Day of Action for Women’s Health by women’s health advocates. The main objective of this day is to raise awareness on the issues related to women’s health and well-being such as Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights (SRHR). The coordination of the International Day of Action for Women’s Health is done by the Women’s Global Network for Reproductive Rights (WGNRR). May 28th is a Day of Action recognized internationally wherein any organisation or individual can mobilise their communities around their own priority topic best suiting the local context.

Source: http://www.may28.org/
https://www.nhp.gov.in/International-Day-of-Action-for-Womens-Health-2016_pg
Image of the Day Zombie Fires
This is the satellite image of what is called as “zombie fires”, which are the remnants of burns from the previous year that somehow stayed alive, smouldering underground, through the long, cold winter. Zombie fires in the Arctic are linked to climate change. Hotter summers and longer burn seasons mean fires from the previous year may come back to life the following spring. The reason for such fires lies in the huge presence of peat in the Arctic. Once it is on fire, peat can provide a habitat for fires to smoulder on long after their surface flames have abated—for days, weeks, months, or even years.

Ricochet Impact
- Context: IMF has warned of Ricochet Impact due to unequal global recovery.
- Ricochet Impact, also known as transfer effect, in this context, refers to the negative impact on the one who helps others.
- IMF has warned for Ricochet Impact on advanced economies as the emerging-market nations’ struggle to come out of the pandemic-induced economic crisis can spill over to hurt the developed world.
- Poorer nations are faced with the risk of interest rates increasing while their economies experiencing little or no growth.

Primary source: https://www.livemint.com/news/imf-head-warns-of-ricochet-impact-of-uneven-global-recovery-11621970922514.html
Growth in Freight Traffic of Indian Railways
- Context: The Railways has recorded more than 10% increase in freight loading as compared to normal year of 2019-20.
- Several concessions/discounts are being given in Indian Railways to make railways freight movement attractive.
- Over the last 18 months, freight speed has doubled in Indian Railways. Around six zonal railways have registered average speed of freight trains above 50 Km per hour.
- Long term tariff contract with major customers envisages growth and retention of traffic by offering incentive over benchmark.

National Mission on use of biomass in coal based thermal power plants
- Context: Ministry of Power has decided to use biomass in coal based thermal power plants.
- It will contribute to the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP), energy transition in the country
- The mission aims to address the issue of air pollution due to farm stubble burning and to reduce carbon footprints of thermal power generation.
- The Mission’s objectives include:
- Increase the level of biomass co-firing from present 5% to higher levels
- R&D in boiler design to handle the higher amount of silica, alkalis in the biomass pellets
- Facilitate overcoming the constraints in supply chain of biomasspellets and agro-residue

Primary source: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1721473
https://www.ecowatch.com/chatham-house-biomass-study-2288764699.html
New Rules for Increased FDI in Insurance Sector
- Context: The Ministry of Finance hasamended Indian Insurance Companies (Foreign Investment) Rules, 2015 and clarified final rules for increased FDI in Insurance Sector.
- Amendment will give effect to 74 per cent FDI limit.
- Highlights of the New Rules:
- Management Persons to be Resident Indian Citizens
- Meaning of Foreign Investment: Total foreign investment = direct+ indirect foreign investment.
- Direct investmentby a foreigner will be called foreign direct investment
- Investment by an Indian company(which is owned or controlled by foreigners) into another Indian entity is considered as indirect foreign investment.
- Significance:
- inclusion of global best practices
- innovative insurance products, reduced cost of insurance
- additional capital inflow will help to push growth
- increase competition in the sector
- improve insurance penetration level
Primary Source: https://indianexpress.com/article/business/banking-and-finance/insurance-fdi-rules-set-govt-looks-to-whet-investor-appetite-7330392/
Addressing vaccine hesitancy- TH
Essence: COVID-19 vaccines have been developed at a record pace, thanks to the collaborative efforts of governments, industry, academia, and other organisations. But there seems to be problem in vaccinating people against COVID-19. This article emphasises on urgently addressing the issue of vaccine hesitancy while listing down the reasons for the same.
Why you should read this article?
- Know about the vaccine hesitancy and the influencing factors such as lack of awareness of the extent of benefits, fears based on inaccurate information, lack of access to vaccine, civil liberty concepts, cost, cultural issues, and various layers of confidence deficit (mistrust of intent, lack of confidence in the system) sown by conspiracy theories and disinformation.
- Identify steps which needs to be taken urgently to allay vaccine fears for instance focusing on simple facts, providing practical information through social media, alternatives to apps for those lacking easy access to vaccines, and taking the help of well-informed frontline workers.
Article Link: https://www.thehindu.com/todays-paper/tp-opinion/addressing-vaccine-hesitancy/article34662478.ece
Re-arming the global health order- HBL
Essence: Editorial is discussing the need of a global order to mitigate & manage potential threats to global health. This regime should specifically include obligations of the member countries to provide information, data, and subject themselves to an independent audit or evaluation much in the same manner as the obligations of the member countries under the IMF/UN/FATF systems.
When the global diplomatic community met to shape the UN in 1945, one of the areas discussed was a global health body. The World Health Organisation (WHO) came into being in 1948. There is an urgent need to extend the application of Chapter VII of the UN Charter, which charts out a course for “action” with respect to threats to the peace and aggression, without which the WHO is a toothless body.
If implemented, this will pave the way for enforcing an internationally coordinated and supervised approach with a view to ensuring the safety of public health.
Why you should read this ?
- To get insights into the impact of covid on global health system.
- To understand the mechanisms which can be adopted for advancing global health order.
- To know about the evolution of WHO & emergent need to give more powers on the line of FATF.
- To get insights into the WHO efforts to identify the origin of Covid-19 virus & debate around it.
Article Link: https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/opinion/re-arming-the-global-health-order/article34660110.ece
Unique Tribal Traditional of India: The Gowda Tribe in Goa
About Gowda Tribe:
- The Gowda tribe is considered progressive because of distinct characteristics like Women Empowerment and Religious Harmony.
Women Empowerment:
- The women of this tribe are given a wide range of rights, from economic to social to political matters, which is exceptionally progressive for a primitive tribe.
- They are so progressive that after their husbands’ deaths, widows inherit their deceased spouse’s property - a remarkable tradition that does not translate to most other Indian tribes or even India as a whole.

Religious Harmony:
- The second unique attribute of the Gowdas is their religion and their faith.
- They were originally Hindu, the Portuguese forcibly converted them to Christianity in 1620’s.
- But now, they follow the best practises from both the Hindu Tradition and Christianity displaying a beautifully harmonious co-existence of two differing religions.
Lessons to be learnt: Appreciating the tribal diversity, their practices, and beliefs. Some of the practices are more modern in nature than the present day followed norms.
Where can this case study be used: Unique Tribal Traditional of India, Examples of religious harmony in India.
Share the article
Get Latest Updates on Offers, Event dates, and free Mentorship sessions.

Get in touch with our Expert Academic Counsellors 👋
FAQs
UPSC Daily Current Affairs focuses on learning current events on a daily basis. An aspirant needs to study regular and updated information about current events, news, and relevant topics that are important for UPSC aspirants. It covers national and international affairs, government policies, socio-economic issues, science and technology advancements, and more.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs provides aspirants with a concise and comprehensive overview of the latest happenings and developments across various fields. It helps aspirants stay updated with current affairs and provides them with valuable insights and analysis, which are essential for answering questions in the UPSC examinations. It enhances their knowledge, analytical skills, and ability to connect current affairs with the UPSC syllabus.
UPSC Daily Current Affairs covers a wide range of topics, including politics, economics, science and technology, environment, social issues, governance, international relations, and more. It offers news summaries, in-depth analyses, editorials, opinion pieces, and relevant study materials. It also provides practice questions and quizzes to help aspirants test their understanding of current affairs.
Edukemy's UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through:
- UPSC Daily Current Affairs can be accessed through Current Affairs tab at the top of the Main Page of Edukemy.
- Edukemy Mobile app: The Daily Current Affairs can also be access through Edukemy Mobile App.
- Social media: Follow Edukemy’s official social media accounts or pages that provide UPSC Daily Current Affairs updates, including Facebook, Twitter, or Telegram channels.

.gif)